Docker is an open platform for developing, shipping, and running applications. It enables you to separate your applications from your infrastructure so you can deliver software quickly. With this, you can manage your infrastructure in the same ways you manage your applications. By taking advantage of Docker’s methodologies for shipping, testing, and deploying code quickly, you can significantly reduce the delay between writing code and running it in production.
The way Docker works
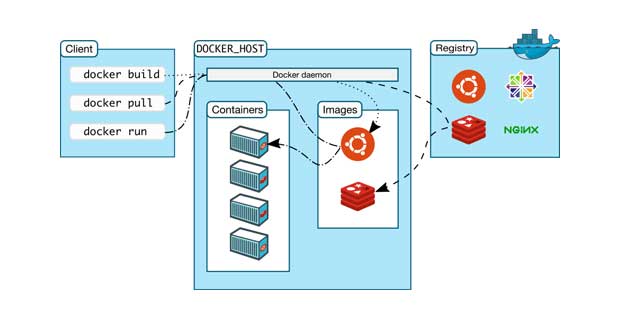
It uses a client-server architecture. The Docker client talks to the Docker daemon, which does the heavy lifting of building, running, and distributing your Docker containers. The Docker client and daemon can run on the same system, or you can connect a Docker client to a remote Docker daemon. The Docker client and daemon communicate using a REST API, over UNIX sockets or a network interface.
Docker Installation
Click here and create your own Docker Hub account and download your machine’s operating system supported docker and install in your local machine.
Check docker version after installation
docker -vDocker Commands
docker helpSo it will return all docker commands but some usual common docker commands given below –
Verify your Networks
networetwork lsStart docker containers
docker-compose up or docker-composer up -dStop and remove our docker container
docker-compose downCreate our Docker image from our Dockerfile
docker build --tag my_httpShow the running containers
docker psStopping a running container
docker stop CONTAINER_IDStop all running container
docker container stop $(docker container ls -aq)Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Delete all running containers
docker container rm $(docker container ls -aq)Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Delete docker image
docker rmi IMAGE_IDCreate Docker file
FROM nginx
COPY html /usr/share/nginx/htmlCreate Docker image from the Dockerfile
docker build --tag my_http_serverCheck the image has been created
docker imagesRun our docker image on port 8080
docker run -d -p 8080:80 --name my_http_serverCode language: CSS (css)Check my docker is running?
http://localhost:8080Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Stop running container
docker stop CONTAINER_IDFind the running image ID
docker imagesRemove the running image ID
docker rmi my_httpIf removal fails force the removal
docker rmi my_http –forceCreate php Docker file and image build from it
Create php Docker file
FROM php:7.2-cli
COPY ./src /usr/src/myapp
WORKDIR /usr/src/myapp
CMD [ "php", "./docker_index.php" ]Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Create our Docker image from my php Dockerfile
docker build -t run-phpRun my docker image which should have copied a local file called docker_index.php
docker run -it --rm --name run-app run-phpCreate php Dockerfile
FROM php:7.2-apacheCode language: CSS (css)Create my docker-compose file
version: "3"
services:
www:
build: .
ports:
- "8080:80"
volumes:
- ./src:/var/www/html/
networks:
- defaultCode language: JavaScript (javascript)Start my docker container from docker-compose file
docker-compose up
or
docker-compose up - d // detached mode
Note: if there is some help needed for install to create docker image then feel free to contact ixora solution.

Add a Comment